J.F. Quaatz, M. Giglmaier, S. Hickel, N.A. Adams (2014)
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow 49: 108-115. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2014.05.006
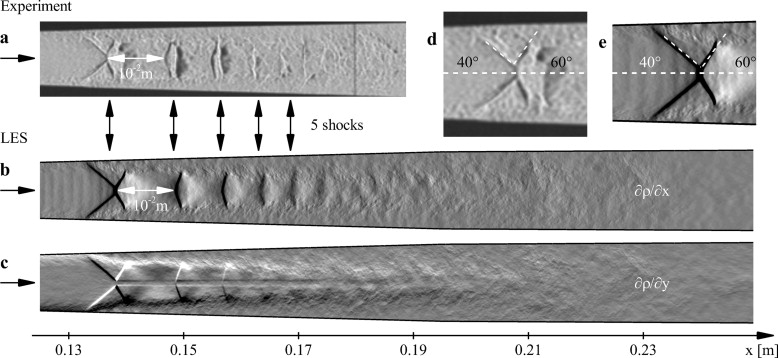
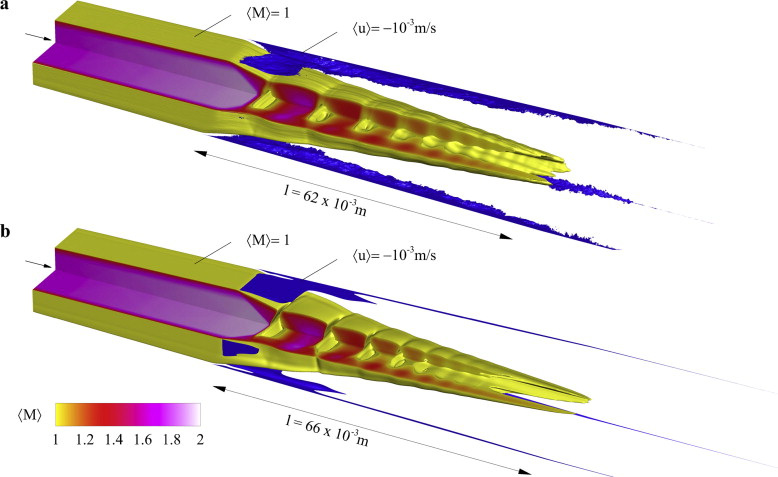
Well-resolved Large-Eddy Simulations (LES) of a pseudo-shock system in the divergent part of a Laval nozzle with rectangular cross section are conducted and compared with experimental results. The LES matches the parameter set of a reference experiment. Details of the experiment, such as planar side walls, are taken into account, all wall boundary layers are well-resolved and no wall model is used.
The Adaptive Local Deconvolution Method (ALDM) with shock sensor is employed for subgrid-scale turbulence modeling and shock capturing. The LES results are validated against experimental wall-pressure measurements and schlieren pictures. A detailed discussion of the complex flow phenomena of three-dimensional shock-wave–boundary-layer interaction, including corner vortices and recirculation zones, is presented. Limitations of RANS approaches are discussed with reference to the LES results.